Linux is a developer-friendly operating system, with approx 4% market share and this number continues goes up. It is designed for development environments, because it has the highest stability and reliability to deal with high workloads. There are many Linux distros tailored for different usage, such as Mint, Ubuntu, Nitrux, etc. And you can install Linux on a server or via virtual machine.
While running Linux on your machine, no matter on a PC, Mac or others, accidentally deleting files is not uncommon. In this guide, we will show you how to recover recently or permanently deleted files in Linux Mint, Ubuntu or other distributions.
Yes, it is.
Like other operating systems, Linux is loaded and run on a disk that offers enough space to write and read data. Though unlike macOS or Windows that saves files in a folder, Linux saves its files in the root directory. When a file is deleted from Linux, it becomes invisible in the root directory because the link to this file is removed, but it is still stored in the original space, until there is new data written to Linux and replace. Therefore, as long as the deleted file is not overwrite by new data, it is still possible to recover, using commands or professional data recovery programs.
There are a lot of Linux distros, if you are using a distribution that has a desktop environment and deleted the files by moving to Trash bin without further deletion, the files will be kept in recycle bin until the disk becomes full.
If you don’t use the desktop environment and deleted the files with rm command on a PC or Mac, the files won’t be moved to recycle bin, because there is no recycle in on your device. Though you cannot find the deleted files under this situation, they are still stored on your Linux, until they are overwritten by new data.
In exploring the recovery of deleted Linux files, we should consider how the files were deleted. And before restoring the files, we need to unmount the partition where the deleted files were stored. This stops new data overwriting the deleted files and increases the chances of a file recovery, here is how:
Find the terminal launcher in your Linux distribution and enter the following commands:
sudo umount /dev/sdXY
sudo mount -o ro /dev/sdXY /media/read-only
You need to replace X with your Linux drive letter (A/BC/...) and Y with the Linux partition identifier(1/2/3/...) that stored the deleted files.
Now, we will look at 4 ways to recover deleted Linux files, with or without commands.
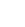
If you have installed SSH service on Linux, you can remotely connect to the Linux server and recover the deleted files with ease, by using Cisdem Data Recovery.
Cisdem Data Recovery Windows is designed to recover recently & permanently deleted, lost, formatted, damaged, even unsaved files from both internal hard drive and external storage device that connects with the PC. Being a reliable data recovery program, it applies to different data loss scenarios and supports a lot of file types. What makes it excel others is its rich recovery modes, in the latest V18.0.0, it add support for Linux recovery.
Main Features of Cisdem Data Recovery
 Free Download Windows 11/10/8/7
Free Download Windows 11/10/8/7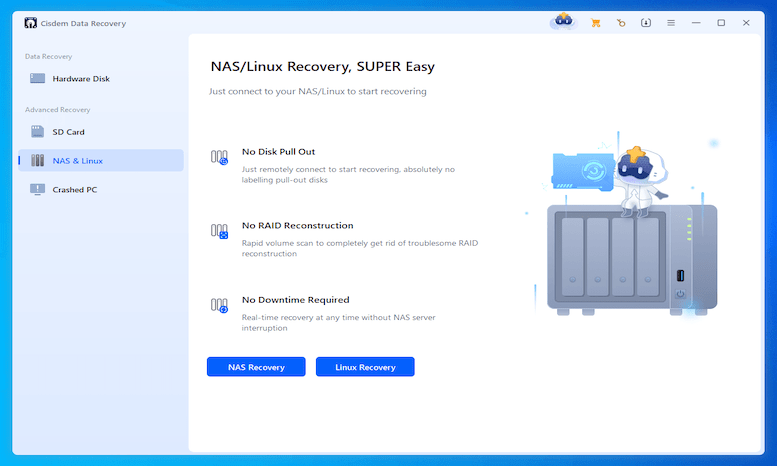
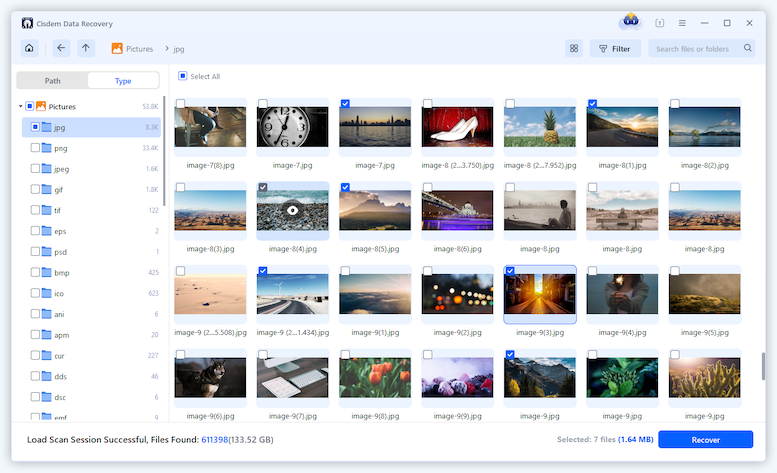
If you are using a Linux distribution with desktop environment,such as Ubuntu, the deleted files will be moved to the trash folder, you just need to open the Trash app and put the files back.
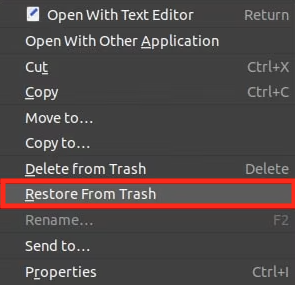
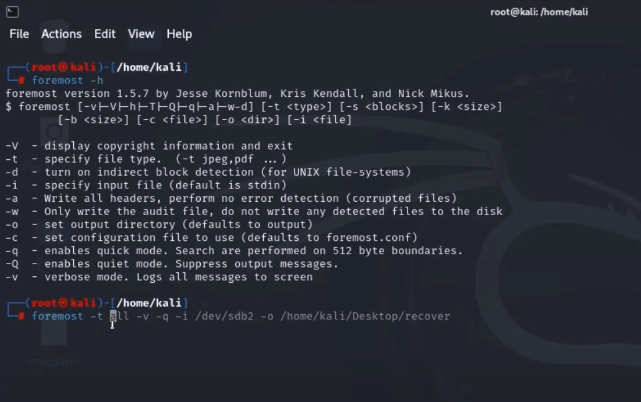
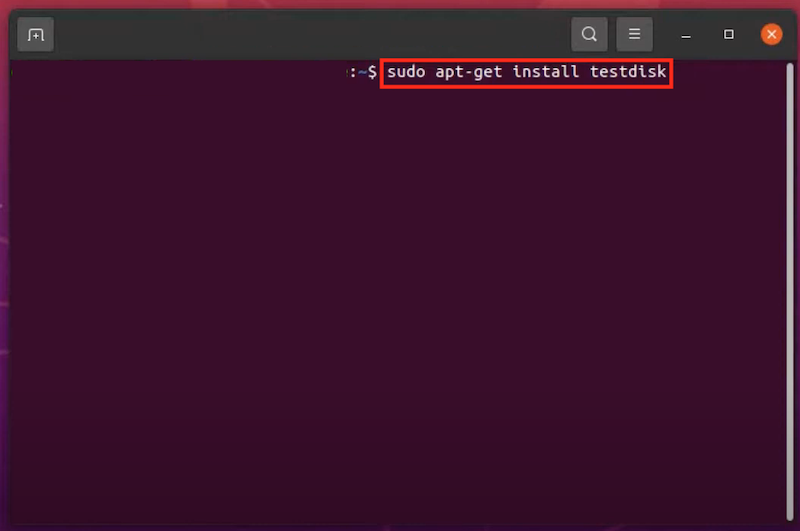
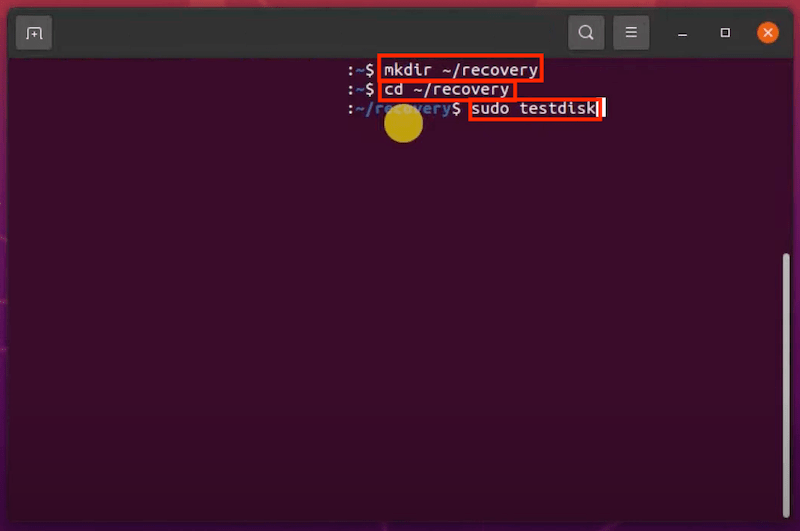
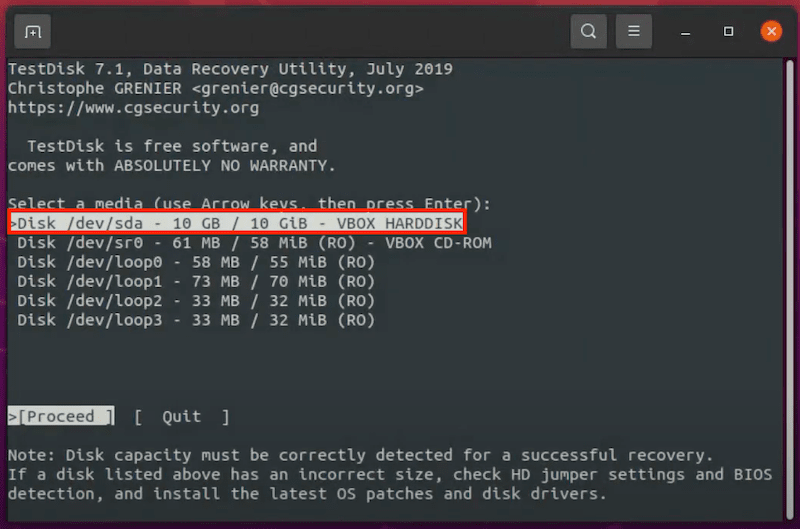
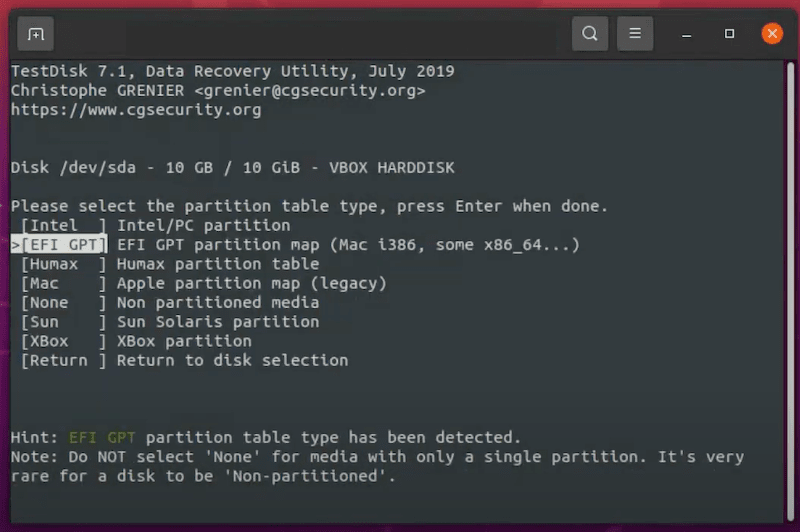
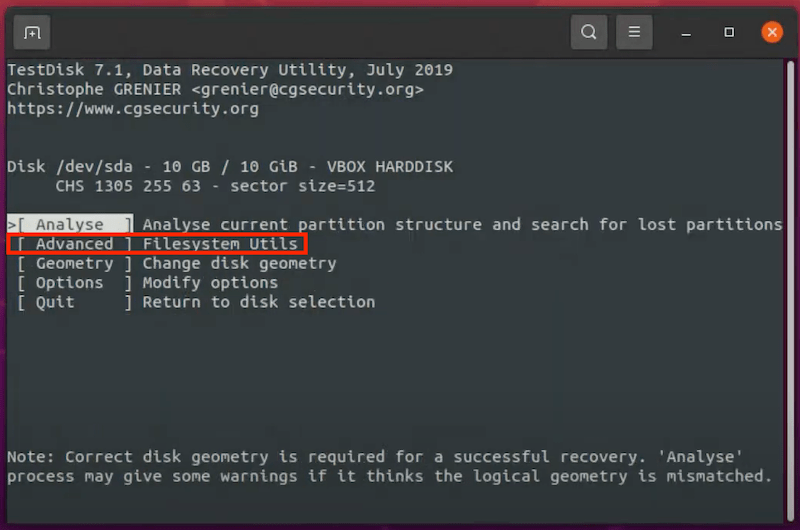
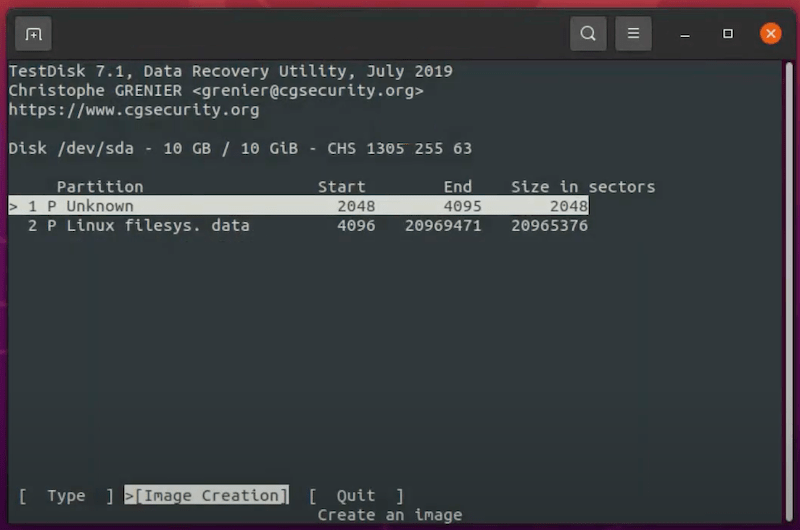
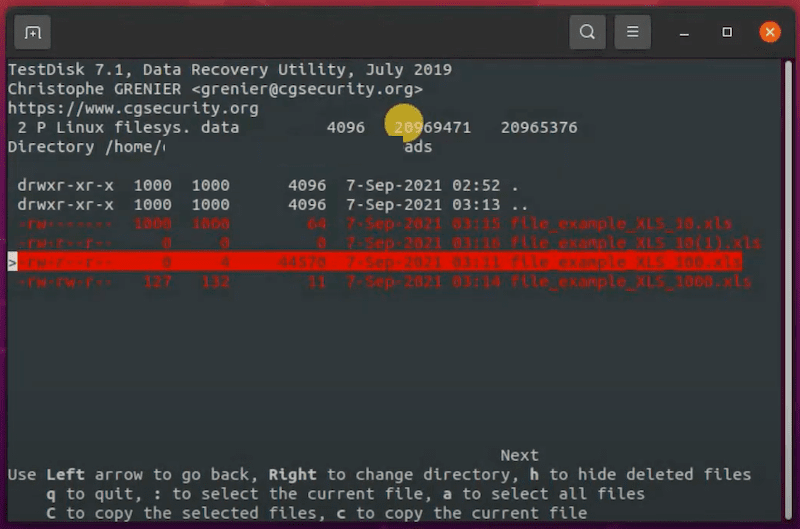
If your Linux distribution doesn’t come with a desktop environment, you can undelete Linux files using commands in Terminal or other command launchers on your device, but you have to install Linux a data recovery program. Luckily, there are so many free Linux data recovery apps for your option, here we recommended the best 2: Foremost and Test Disk.
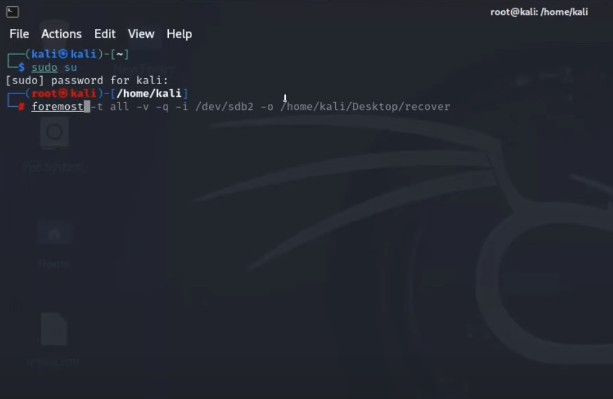
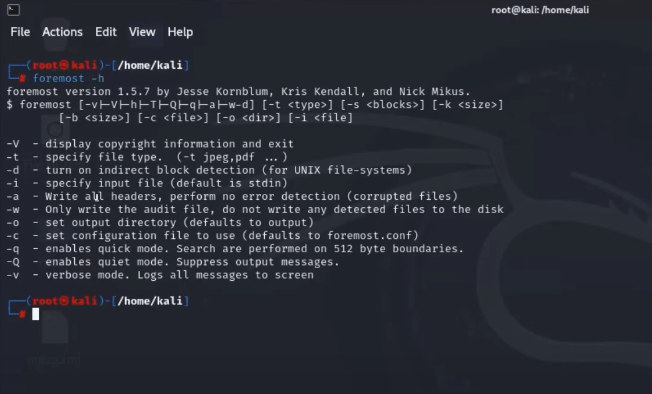
Or if you have a backup for the Linux files, on external hard drive or up in the cloud, you can restore the deleted Linux files via the backup.
Time Machine is the free backup and restore utility on Mac, if you have enabled this feature on your device, it is possible to restore the deleted Linux files from the backup.
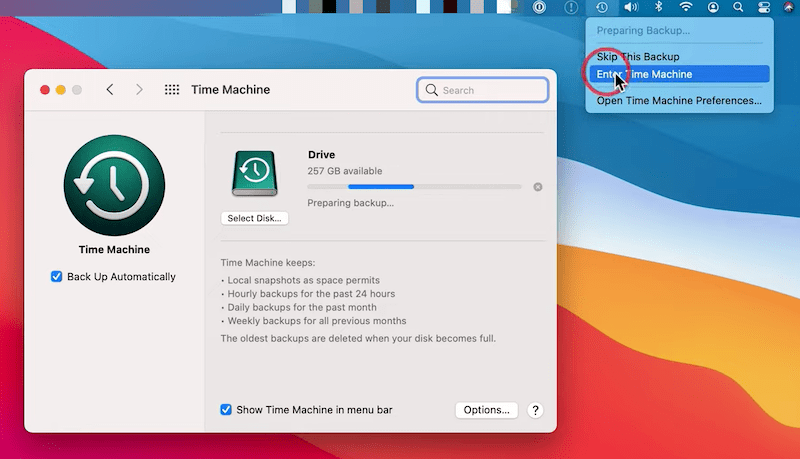
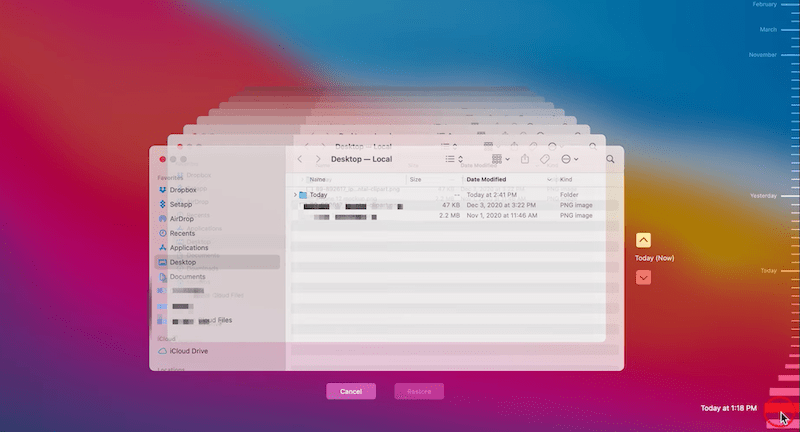
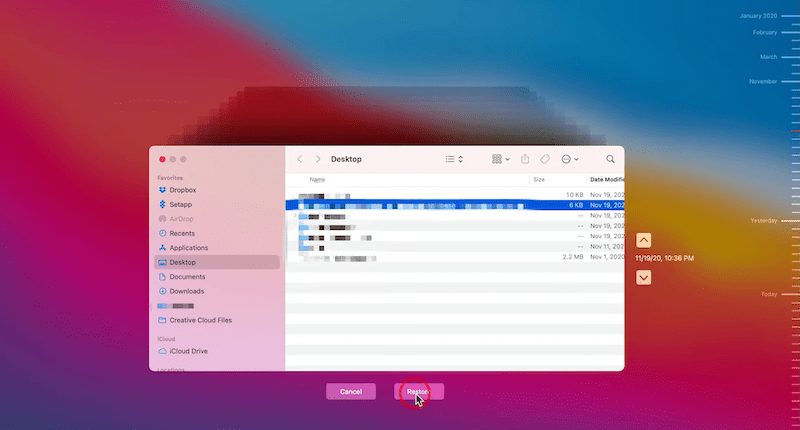
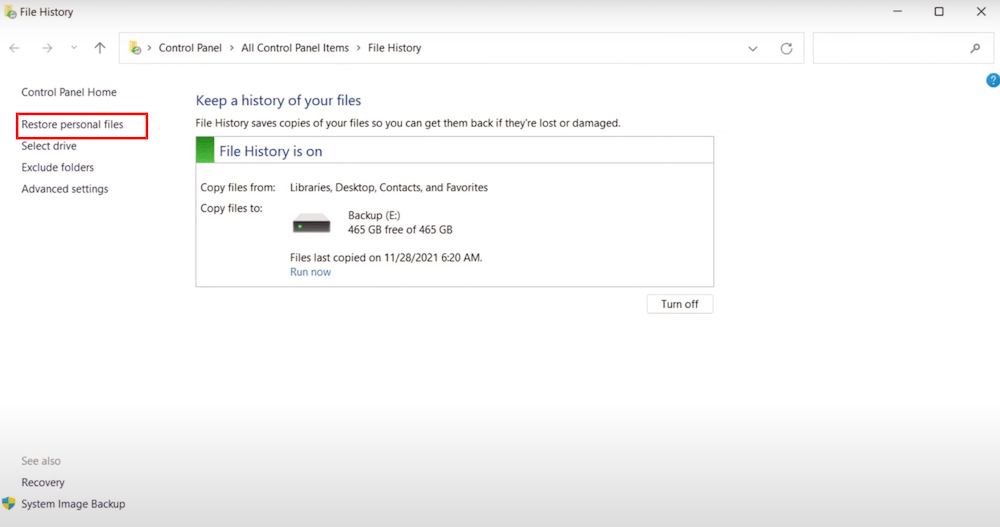
On Windows, the backup and restore utility is File History, if you have enabled the auto backup feature in this tool, you will be able to restore the lost Linux files from the backup.
If you have uploaded a copy of the Linux files to your Google Drive or other cloud storage accounts, you can sign in those services and re-download the deleted files to your device. Here we take Google Drive as an example.
Recovering deleted files from Linux can be different from each other according to the Linux distros, if yours are the same as in our recovery process, just follow the steps. But if you are using other Linux distros and don’t how to restore the files, you can leave us a message in the comment, we will get back to you as soon as possible. Or actually, as long as you know the syntax to restore files with commands on Linux, it is quite easy for Linux file recovery, also, there are many video tutorials on YouTube for your reference.

Zoey shows a great interest in what she does. Although not long with Cisdem, she has possessed a professional understanding of data recovery.

